OSPF
Stands for "Open Shortest Path First."
OSPF is a routing protocol that helps routers inside the same network automatically find the best paths for sending data. It is an open standard created by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and is widely used in large enterprise and campus networks today.
OSPF works by letting each router share information about the network's layout with its neighbors. Using this data, every router builds the same "map" of the network. Then, each router uses the "Shortest Path First" algorithm to figure out the quickest and most efficient route to every destination.
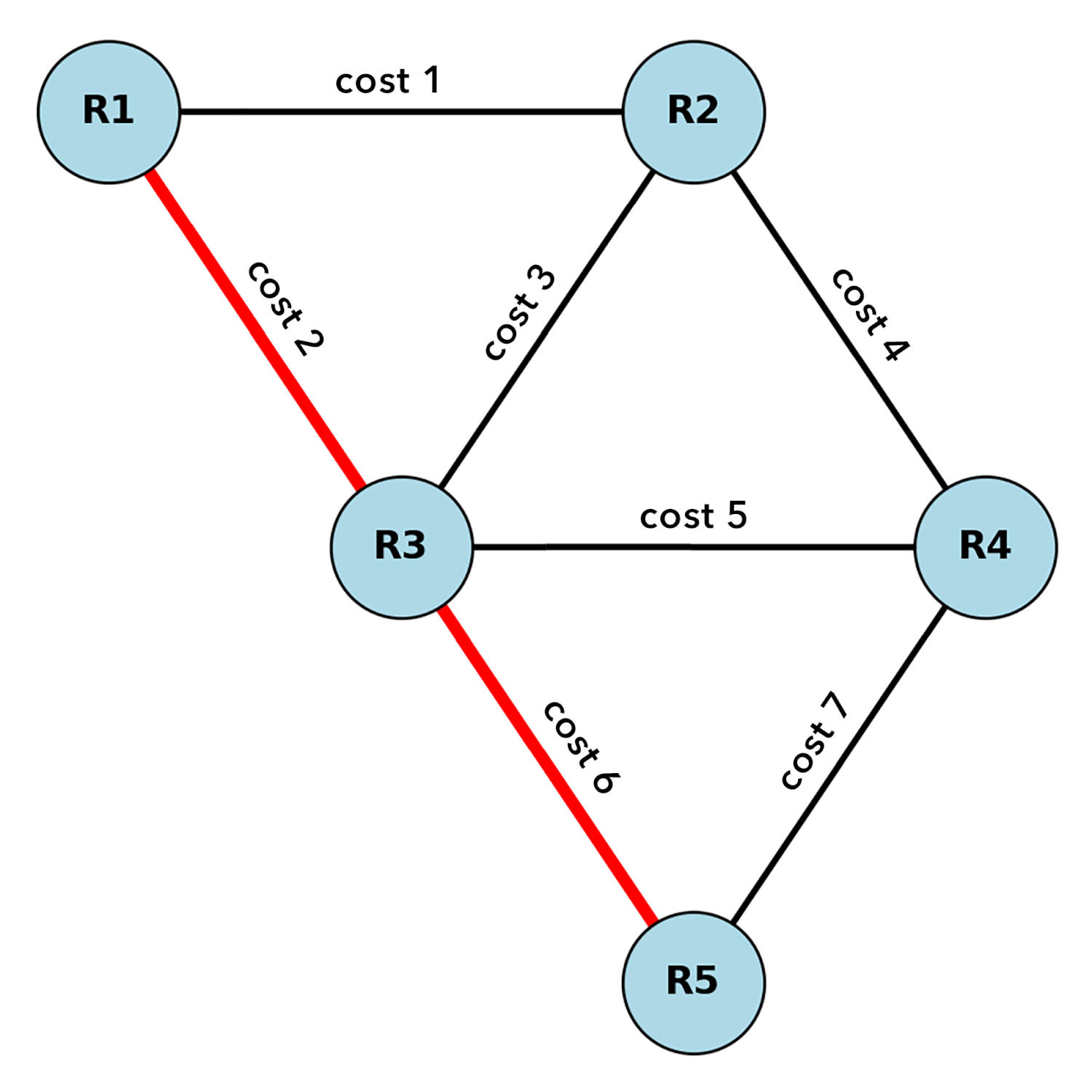
The diagram above shows how OSPF works. Five routers are connected in a mesh, and R1 needs to send data to R5. Before sending the data, OSPF calculates the fastest route based on link "costs" between each node. R1 to R3 to R5 (shown in red) is the quickest route since it has the lowest cost (cost 2 + cost 6). However, if R3 were a long distance from R1 and R5, the cost may be less via another route, even if it required more hops.
When a network change occurs — such as a link going down or a new router being added — OSPF quickly updates the network map. It then finds a new best path, often in seconds, without manual changes.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge